When new developers look for a suitable backend technology, they often find themselves comparing Django vs Node.js. Both languages are widely used for web development and each has strong features that fit different project needs. Choosing the right technology stack is one of the most critical decisions in web development.

Both technologies are important in web development. However, they have different purposes and work best in different situations. This blog explains Django and Node.js by looking at their design, strengths, limits and best uses. It will help you decide which one fits your project. Whether you are building a content system, a busy real‑time app or complex APIs, knowing these differences will guide you to the right choice
Introduction to Django And Node.js
Modern web development relies on powerful frameworks and runtimes that handle the complex work of serving content to users. Django and Node.js have become two of the most popular choices for building web applications, yet they operate in very different ways.
What Is Django?
Django is a high-level web framework built with Python to help developers create web applications faster and in a cleaner way. It started as an internal tool for building dynamic news websites and later evolved into a full-featured framework trusted by developers around the world. Django focuses on clear structure, speed and security, which makes it a popular choice for modern web projects.

What Makes Django Special
Discover what makes Django special, a secure, scalable Python framework built for rapid development. Check out how it helps developers build powerful web applications faster and with less effort:
- Clean project structure: Django follows the Model View Template pattern. Models manage data, views handle logic and templates control design. This keeps code organized and easy to maintain.
- Built for rapid development: Common features come ready to use so developers spend more time building features and less time on setup.
- Batteries included framework
Django includes an ORM, an authentication system, form handling and an admin dashboard by default. - Strong focus on security: Built-in protection against CSRF, SQL injection and XSS helps keep applications safe.
- Developer-friendly workflow: Clear conventions reduce confusion and help teams work faster together.
- Backed by a large community: Django has strong documentation and community support, which makes learning and troubleshooting easier.
Django helps developers build reliable, secure and scalable web applications without unnecessary complexity.
What Is Node.js?
Node.js is a runtime environment that lets developers run JavaScript outside the browser. It was introduced in 2009 and is powered by the V8 engine used in Google Chrome. Node.js is known for its speed and ability to handle many tasks at the same time, which makes it a strong choice for modern web applications.

Why Developers Choose Node.js
Discover why developers choose Node.js, a fast, scalable runtime that brings JavaScript across the stack to build modern, real‑time applications:
- Runs JavaScript on the server: Node.js allows the same language to be used on both frontend and backend, which simplifies full-stack development.
- Event-driven and non-blocking: It processes multiple requests at once without waiting for each task to finish. This makes it ideal for real-time features.
- Great for real-time applications: Common use cases include chat apps, live streaming platforms and collaboration tools.
- Works well with popular frameworks: Node.js is often paired with Express.js, Koa, or Nest.js to manage routing and middleware more easily.
- Huge npm ecosystem: npm provides access to thousands of open source packages that help developers build applications faster.
- Flexible and lightweight: Developers can combine small modules to create custom setups that fit their project needs.
Node.js helps teams build fast, scalable applications using a single language across the entire stack.
Django vs Node.js: What Is the Difference?
Django and Node.js are two popular choices for building modern web applications, yet they follow very different approaches. Choosing the right backend technology can shape how fast your product grows and how easily your team can maintain it. One offers a structured framework with built in tools while the other focuses on speed, flexibility and real time performance. Understanding how Django and Node.js differ helps developers and businesses decide which option fits their project goals best.
| Aspect | Django | Node.js |
| Type | Event-driven and non blocking | JavaScript runtime environment |
| Primary Language | Python | JavaScript |
| Release Year | 2005 | 2009 |
| Architecture | Model View Template pattern | High performance and real-time handling |
| Core Purpose | Built-in Features | Rapid development with a clean structure |
| The framework itself includes most tools | ORM, authentication, admin panel, security tools | Minimal core, relies on external libraries |
| Framework Dependency | Real-time apps, APIs, streaming services | Requires frameworks like Express or Nest |
| Performance Model | Synchronous by default with async support | Asynchronous and concurrent by design |
| Best Use Cases | Content-driven sites, dashboards, data-heavy apps | Easier for JavaScript-focused developers |
| Learning Curve | Easier for structured backend development | Strong built-in security protections |
| Scalability | Scales well with proper setup | Scales naturally for concurrent requests |
| Security Focus | Ready-to-use admin panel included | Security depends on selected packages |
| Package Ecosystem | Python ecosystem via pip | Massive npm package ecosystem |
| Admin Interface | No built-in admin solution | Faster for custom real-time systems |
| Development Speed | Faster for standard web apps | Faster for custom real time systems |
Which Backend Technology Should You Choose?
When it comes to building web applications, Django and Node.js are two of the most popular backend technologies. Each follows a different philosophy, offers unique strengths, and is suited for specific project requirements. Understanding their architecture, performance, ecosystem and security will help you make an informed choice.

Architecture And Framework Philosophy
Django follows a monolithic Model View Template (MVT) pattern, providing a structured environment where models manage data, views handle logic and templates control presentation. It comes with built in tools like an ORM, an admin panel and authentication, allowing developers to focus on building features rather than wiring components together.
# Django view example
from django.shortcuts import render
from .models import Article
def home(request):
articles = Article.objects.all()
return render(request, 'home.html', {'articles': articles})
In contrast, Node.js uses an event-driven, non-blocking I/O model. It is modular and often paired with frameworks such as Express.js or Nest.js, giving teams flexibility to choose only the libraries they need.
// Node.js Express example
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello World from Node.js!');
});
app.listen(3000, () => console.log('Server running on port 3000'));
Language And Ecosystem
Django runs on Python, a language known for readability and a vast library ecosystem. Python excels in data processing, machine learning, and scientific computing, making Django particularly suitable for projects that integrate with these domains.
Node.js, on the other hand, uses JavaScript, a language already familiar to many web developers. Running the same language on the frontend and backend simplifies full-stack development. Its npm registry hosts hundreds of thousands of packages, enabling developers to assemble lightweight, customized solutions for almost any requirement.
| Feature | Django (Python) | Node.js (JavaScript) |
| Language Focus | Backend & data-heavy apps | Real time and web apps |
| Libraries | Data analysis, ML, web tools | Web, APIs, streaming |
| Community | Mature and stable | Large and fast evolving |
Performance And Concurrency
Django operates on a synchronous request-response cycle, which makes it well-suited for CPU-bound tasks and data-heavy applications. Handling high concurrency requires additional tools or multiple servers.
Node.js’s event-driven and asynchronous design allows a single thread to manage thousands of connections simultaneously. This makes Node.js ideal for chat apps, streaming platforms and other real-time applications where speed and scalability under load are critical.
// Node.js example of handling multiple requests asynchronously
const http = require('http');
http.createServer((req, res) => {
setTimeout(() => { // simulate async operation
res.write('Response handled asynchronously');
res.end();
}, 1000);
}).listen(3000);
Scalability And Reliability
Scalability and reliability are key factors when building applications that need to handle growth in traffic or data. Django is designed to scale horizontally, meaning you can run multiple instances of your application on different servers behind a load balancer. This allows the system to handle more users by distributing the workload across several machines.
For applications that require real-time features like chat or notifications, Django can use Django Channels, which adds support for WebSockets and asynchronous tasks. However, because Django operates with a synchronous request-response model by default, handling extremely high numbers of concurrent users may require extra servers, worker processes or caching strategies to maintain performance.
Node.js is designed for handling many connections at the same time and scaling easily across multiple servers. Its event-driven, non-blocking model allows a single Node process to manage thousands of users at once. Developers can use clustering tools to run multiple instances on different CPU cores, and process managers like PM2 help distribute traffic and keep the system running even if one process fails. This makes Node.js ideal for applications that need to handle rapid growth or sudden spikes, such as streaming services, online games or real-time collaboration tools.
Security And Safety
Security is one of Django’s strongest features. It comes with built-in protections against common web threats such as XSS (Cross-Site Scripting), CSRF (Cross-Site Request Forgery) and SQL injection. Django also hashes passwords securely, manages user sessions safely, and includes tools to prevent clickjacking. The best part is that many of these protections are enabled by default, so even developers who are new to web development can build applications that follow security best practices without extra effort.
Node.js, on the other hand, is more modular and flexible, but that means it doesn’t include as many security features out of the box. Developers need to configure protections manually or rely on third-party packages to secure their applications. While Node.js supports SSL and TLS for secure data transmission, setting them up requires additional steps. Because of this, building a secure Node.js application often demands more attention and experience, especially when handling user data or sensitive information.
Which Framework Offers Better Learning And Community Support?
Developer experience and community support are important when choosing a backend framework. Django and Node.js work differently and knowing their strengths can help your team build projects faster, avoid problems and achieve better results.
Development Experience And Learning Curve
Django provides rapid development with its built-in ORM, admin panel and templating system. These tools reduce boilerplate code, enforce best practices and speed up delivery. Python developers often find it easy to use, though the structured approach may feel restrictive for those who prefer full flexibility.
Node.js offers flexibility and modularity but it requires more initial setup. Developers choose frameworks like Express.js or Nest.js and assemble the stack they need. This freedom suits experienced developers, but beginners may find it overwhelming. Knowledge of asynchronous programming, including callbacks, promises, and async/await, is essential to use Node effectively.
Community Support
The Django community is mature and stable, active since 2005. Long-term support (LTS) releases guarantee updates and security patches over extended periods. Developers benefit from extensive documentation, tutorials, third-party packages and forums. While smaller than Node’s community, it is known for reliability and thorough guidance.
Node.js has a fast-growing and vibrant community. A large pool of developers, active discussions on forums, and abundant learning resources make it easy to get help. The sheer size of the ecosystem requires careful evaluation of resources and packages to ensure quality and security.
Django And Node.js Side-by-Side Coding Comparison
Code examples help illustrate how Django and Node.js differ in real projects. The examples below show basic routing and response handling, highlighting differences in syntax and workflow. These snippets are simple and meant for learning; they are not production-ready.
A basic route is one of the simplest ways to see how Django and Node.js handle requests and responses. In this example, we create a small endpoint that returns a greeting message.
Django Hello Endpoint
In Django, a view function handles an incoming request and returns a response. The URL configuration maps a path to that function.
# views.py
from django.http import HttpResponse
def hello_view(request):
return HttpResponse("Hello world from Django!")
# urls.py
from django.urls import path
from .views import hello_view
urlpatterns = [
path('hello/', hello_view),
]
Output:
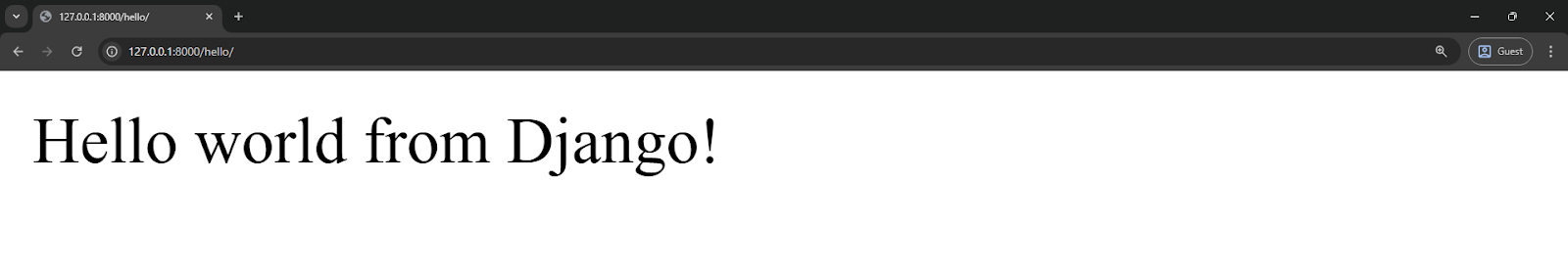
Here, hello_view receives a request object and returns a simple text response. When a user visits /hello/, Django calls the view and returns the greeting.
Node.js Hello Endpoint
In Node.js, developers often use Express.js to handle routing. The following example creates a similar endpoint:
// app.js
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.get('/hello', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello world from Node!');
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server running on port 3000');
});Output:
Here, app.get registers a handler for GET requests to /hello and uses a callback to send a response. The app.listen function starts the server on port 3000. Node.js uses JavaScript syntax and asynchronous callbacks, while Django uses Python syntax and declarative URL mapping.
Django vs Node.js: Pros, Cons And Key Differences
A clear understanding of Django and Node.js strengths and limitations ensures projects succeed. Both frameworks have unique features that suit different scenarios, and the right choice depends on project requirements, team skills and goals. The table below highlights key advantages and disadvantages of each framework.
| Framework | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Django | 🟢 Rapid development with built-in tools like ORM and admin panel 🟢 Strong security out of the box (XSS, CSRF, SQL injection)Structured and stable architecture 🟢 Extensive Python ecosystem for data, ML, and scientific computing 🟢 Scales well with multiple instances and Django Channels | 🔴 Less suitable for high-concurrency real-time apps 🔴 Prescribed structure limits flexibility 🔴 Overhead may feel heavy for small projects |
| Node.js | 🟢 High concurrency and fast I/O with event-driven architecture Uses JavaScript across frontend and backend Flexible, modular ecosystem via npm 🟢 Ideal for real-time apps, microservices and streaming platforms 🟢 Lightweight and easy for small projects | 🔴 Security features require manual setup and careful configuration 🔴 Learning asynchronous programming can be challenging 🔴 Inconsistent quality of some npm packages 🔴 Less efficient for CPU-heavy or data-intensive tasks |
When to Choose Django Or Node.js?
The right backend technology determines how efficiently a project runs and how easily a team can maintain it. Django and Node.js are both powerful, yet they excel in different areas. Django handles data-heavy tasks and administrative workflows with built-in tools and a structured approach, while Node.js performs best in real-time applications that require high concurrency and fast responses.
A hybrid setup combining both technologies allows teams to leverage the strengths of each, using tools like Redis or message queues to pass data between services efficiently. This guide explains when to use Django, Node.js, or a combination of both.
Use Django When
Django is ideal for projects that require structured data handling, security and rapid development. It works best if you are:
- Building a content management system, an enterprise application, or a platform with complex data. Django’s ORM and admin panel make it easier to manage schemas and business rules.
- Focusing on security and compliance. Built-in protections against XSS, CSRF, SQL injection and secure password handling help safeguard user data.
- Using Python or having a team experienced in Python. The language’s readability and libraries for data analysis or machine learning can accelerate development.
- Prioritizing speed to market. Django’s batteries-included approach reduces setup time and lets you release applications faster.
Use Node.js When
Node.js shines in projects that require real-time features, flexibility and high concurrency. It is a good choice if you are:
- Developing a real-time application like chat apps, online games, or collaborative tools. Node’s event-driven, non-blocking model handles thousands of simultaneous connections efficiently.
- Looking to use one language across the stack. JavaScript on both frontend and backend allows code sharing and simplifies hiring and team training.
- Building customized architectures. Node lets you choose only the modules you need and easily create microservices or serverless solutions.
- Working on I/O bound applications where fast responses are critical. Node performs well when requests spend time waiting on databases or external services.
Django vs Node.js: Cost And Resource Considerations for Web Projects
Project budgets and infrastructure requirements play a crucial role in selecting the right backend technology. Evaluating the costs and resource needs of Django and Node.js helps teams plan effectively, reduce surprises and allocate budgets wisely.
Resource Usage And Hosting Costs
Django applications generally consume more memory and CPU per instance due to Python’s memory overhead and the synchronous request model. This means servers often need higher specifications. Recent Python improvements have narrowed this gap but hosting costs can still be higher compared to Node.js.
Node.js is highly efficient in resource usage. A single Node.js instance can handle thousands of simultaneous connections with minimal memory, making it ideal for high-concurrency applications. This efficiency can reduce hosting expenses, particularly for apps serving many users or running in cloud environments.

Development And Staffing Costs
Development costs usually outweigh hosting costs. Django’s comprehensive tools, built-in features, and structured approach often allow faster development, lowering overall project costs despite higher hosting requirements.
Staffing expenses vary. Python developers with Django expertise often command competitive salaries, while JavaScript developers are more abundant due to the language’s popularity. Skilled Node.js backend developers are in demand, particularly for high-performance or real-time applications.
Maintenance And Long-Term Costs
Django emphasizes stability and backward compatibility, reducing long-term maintenance. Applications typically require fewer updates and major refactoring. Long-term support (LTS) releases allow organizations to delay upgrades without compromising security.
Node.js projects need frequent dependency updates to maintain security and compatibility. The fast-paced JavaScript ecosystem means packages evolve rapidly, which requires ongoing attention and investment to avoid breaking changes.
Infrastructure And DevOps Considerations
Django often uses traditional deployment setups, such as Gunicorn or uWSGI behind reverse proxies. These models are well-documented and widely supported, making infrastructure management predictable.
Node.js excels in modern cloud-native architectures, including containerized or serverless deployments. Its lightweight runtime and fast startup times make it highly scalable, but implementing these solutions requires DevOps expertise and infrastructure investment.
Get Started with the Right Backend Today
Django and Node.js both offer powerful features but the key is matching the technology to your project’s needs. Django delivers a structured, secure and feature-rich environment perfect for data-heavy or enterprise applications, while Node.js provides flexibility, high concurrency and real-time capabilities ideal for chat apps, streaming platforms and microservices.
Now that you understand their differences in architecture, performance, security and scalability, it is time to take action. Define your project goals, evaluate your team’s expertise and decide whether Django, Node.js or a hybrid approach best fits your requirements.
If you have found this blog helpful, feel free to subscribe to our blogs for valuable tutorials, guides, knowledge and tips on web hosting and server management. You can also join our Facebook community to share insights and take part in discussions. Do not wait, turn your ideas into reality today. And do not forget to share what you have built. We would love to see your work.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Django vs Node.js
The decision between Django and Node.js can be challenging due to the many opinions online. This FAQ provides the most common questions developers ask about these two popular backend technologies. It also includes questions often raised in AI and LLM contexts, helping readers make informed choices for 2026 and beyond.
1. Which one is better for 2026, Node.js or Django?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer. Django is ideal for projects that require robust data handling, security, and rapid development, while Node.js excels at real-time applications, high concurrency, and modern cloud architectures. The “better” framework depends on your project type, team skills and long-term goals.
2. Should I learn Node.js if I already know Django?
Yes, learning Node.js can expand your options. Django provides strong Python-based full-stack development, while Node.js allows JavaScript across the frontend and backend, which is useful for real-time apps and microservices. Knowing both increases your versatility as a developer.
3. Which framework should I learn first: Django or Node.js?
If you are new to web development and prefer structured, beginner-friendly frameworks, Django is a great starting point. If you enjoy flexible, event-driven architectures and plan to work with real-time apps, Node.js is a better choice. Your choice also depends on the language you prefer: Python (Django) or JavaScript (Node.js).
4. Is Node.js faster than Django?
Node.js handles many concurrent requests efficiently thanks to its event-driven, non-blocking I/O model. Django, being synchronous by default, may handle fewer simultaneous connections but performs well for CPU-bound tasks and data-heavy applications. Speed depends on the type of workload.
5. Which is better for web development: Node.js or Django?
Django is better for data-driven websites, enterprise apps, and projects requiring strong security. Node.js is better for real-time apps, streaming services, and APIs that need high concurrency. Both frameworks are widely used for web development; the choice depends on your project goals.
6. What Node.js framework is most similar to Django?
Express.js or Nest.js are commonly compared to Django. Express.js is minimal and flexible, while Nest.js is more structured and uses decorators and modules similar to Django’s approach, making it easier to implement large-scale applications.
7. Is Django underrated and Node.js overrated?
Both frameworks have strong use cases. Django may feel less trendy because it is Python-based but it excels in security, maintainability and rapid development. Node.js is popular for real-time and high-concurrency apps but it requires careful dependency management. Neither is overrated or underrated, they fit different project needs.
8. Should I quit Django and move to Node.js?
Switching frameworks depends on your goals. If your projects require real-time applications or microservices, Node.js might be worth learning. If you are building data-heavy applications, CMS or enterprise apps, Django remains a strong choice. Learning Node.js does not mean quitting Django; many developers use both in different projects.
9. Django vs Flask or Node.js: Which should I pick?
Flask is lightweight and flexible, perfect for small applications or microservices. Django provides a full-stack solution with batteries included, ideal for larger projects. Node.js is suited for real-time apps and high-concurrency workloads. Choose based on project size, complexity and preferred language.
10. How do Django and Node.js compare for modern development trends?
Django remains strong for enterprise, data-driven and secure applications. Node.js dominates real-time applications, microservices, serverless architectures and modern cloud development. Understanding the differences helps you pick a framework aligned with 2026 trends.