If you have ever clicked a button on a website and watched something happen instantly, you have seen JavaScript in action. JavaScript is a programming language that brings websites to life by adding interactivity and dynamic behavior. It allows developers to create everything from simple animations to complex web applications.

If you are new to the world of web development, you have likely heard this name thrown around. But asking ‘what is JavaScript’ can lead to some confusing technical answers. This guide is here to change that. We will break down the concepts into simple pieces that anyone can understand.
The Core of The Modern Web
The web works as a collaborative effort between three main technologies. HTML structures the content, CSS controls the design and JavaScript adds interactivity. Together, they create the experience you see on your screen.
HTML builds the structure. It puts the text, images and buttons on the page. CSS handles the style. It makes things look good with colors, fonts and layouts. Then comes JavaScript. It brings the page to life. Without it, a website is just a digital poster. With it, a website becomes an application that can think and react.
What Is JavaScript and Why Does It Matter?
JavaScript is a programming language used primarily to make websites interactive. When you visit a page and see moving maps, animated graphics or scrolling video players, that is JavaScript at work. It is a text-based language that allows you to write code that browsers can understand and run.
The importance of this language cannot be overstated. It is one of the three core technologies of the World Wide Web (WWW). Every modern web browser has a built-in engine specifically designed to read and execute JS code. This means you do not need to install special software to run it. It just works right inside Chrome, Firefox, Safari or Edge.
Developers love JavaScript because it is versatile. You can use it to check if a user filled out a form correctly before sending it. You can use it to load new content without refreshing the page. It transforms a static document into a dynamic experience.
Why JavaScript matters for the web:
- It allows pages to respond to user actions immediately.
- It runs directly in the browser, which reduces the load on the server.
- It works perfectly alongside HTML and CSS.
- It is supported by a massive community of developers.
The History And Rise of JavaScript
Brendan Eich created JavaScript in 1995 while working at Netscape Communications. Originally developed in just 10 days, the language was designed to make web pages more dynamic and engaging. Today, JavaScript has evolved into one of the most popular programming languages in the world. According to the Stack Overflow Developer Survey, JavaScript consistently ranks as the most commonly used programming language among developers.
What makes JavaScript unique is its ability to work on both the client side and server side. On the client side, it runs in the browser and controls what users see and interact with on a webpage. On the server side, with the help of environments like Node.js.
JavaScript can handle backend operations like database management and server logic. This versatility means you can use JavaScript to build complete web applications from front to back.
JS follows a simple set of rules called JavaScript syntax basics that determine how code should be written. These rules include how to declare variables, write functions and structure your code properly. Learning these fundamentals helps beginners write clean and effective JavaScript code.
What Is JavaScript Used For?
When people ask what JavaScript is used for, the answer might surprise you. It started as a technology for simple webpage effects, like changing text or creating small animations. Today, it powers almost everything you see and click online. From interactive forms to full web applications, JavaScript brings websites to life and keeps them running smoothly.
You can build full-scale web applications that look and feel like desktop software. Google Maps, Facebook and Twitter are all heavy users of this technology. It handles the constant stream of updates, notifications and real-time interactions.
Beyond websites, JavaScript is now used to build mobile apps. Frameworks allow developers to write code once and deploy it to both iOS and Android. It is even used on servers through environments like Node.js. This means you can use the same language for the front end and the back end of your application.
JavaScript plays a key role across modern technology by supporting a wide range of applications. Such as:
- Brings websites and games to life with real-time interaction
- Runs web servers and supports backend development
- Powers mobile apps on phones and tablets
- Drives smartwatches and Internet of Things devices
How Is JavaScript Used in Web Development?
JavaScript serves many purposes in modern web development. Its primary role is to make websites interactive and responsive to user behavior. When you fill out a form, play a video or see a content update without refreshing the page, JavaScript is working behind the scenes. Some common ways JavaScript is used:
Form Validation
JavaScript checks if users have filled out forms correctly before submitting data. It can verify email addresses, ensure passwords meet requirements and highlight errors instantly without sending information to the server. This saves time and improves the user experience significantly.
Dynamic Content Updates
Websites can update content without reloading the entire page thanks to JavaScript. Social media feeds that load new posts as you scroll, shopping carts that update totals immediately and news sites that refresh headlines automatically all rely on this capability.
Interactive Elements
Dropdown menus, image sliders, tabs, accordions and modal windows are all powered by JavaScript. These elements respond to clicks, hovers and other user actions to create smooth and engaging interfaces.
Animations And Visual Effects
JavaScript can create animations that make websites feel more alive and professional. From subtle transitions to complex animated graphics, the language gives developers control over visual elements and their timing.
Browser Games And Applications
Many browser-based games and web applications run entirely on JavaScript. These range from simple puzzle games to complex productivity tools that work just like desktop software.
JavaScript examples for beginners often start with simple tasks like changing text on a button click or showing an alert message. As you progress, you can build more complex features like calculators, to-do lists and interactive quizzes. The possibilities grow as your skills develop.
Building Web Servers And Server Applications
JavaScript is not limited to the browser. With Node.js, it runs on servers to handle requests, manage databases, and power full backend systems. This makes it a strong choice for building fast and scalable web servers and server applications.
Developers often choose Node.js for APIs, real-time apps and data-driven platforms. Hosting these applications becomes easier with platforms like xCloud, which offers optimized Node.js environments and simple server management. You can deploy and manage Node.js projects smoothly using xCloud’s managed hosting solution.
The language also plays a crucial role in popular frameworks and libraries like React, Angular and Vue.js. These tools build on JavaScript to help developers create sophisticated web applications more efficiently.
How JavaScript Works in Your Browser?
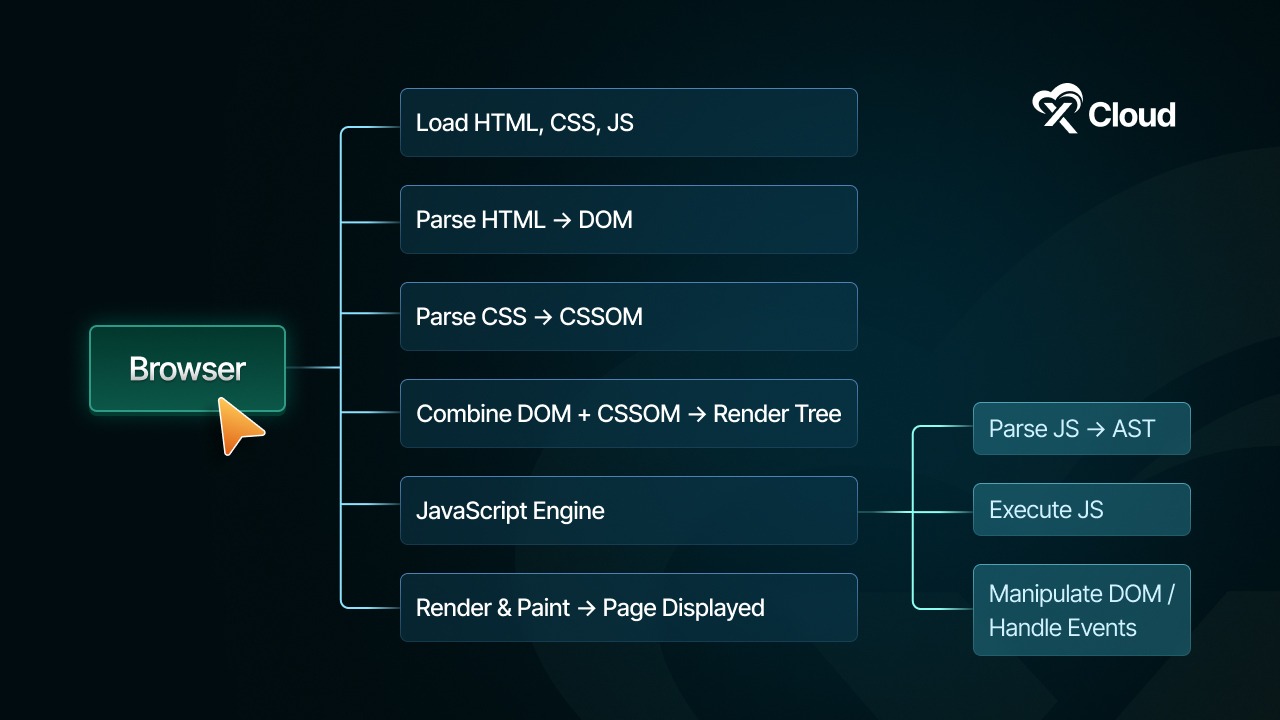
When you visit a website, your browser downloads HTML, CSS and JavaScript files from the server. The browser then interprets and executes the JavaScript code to make the page interactive.
JavaScript is a language that runs in your browser. This means it works on your computer, not on the server. Because of this, actions happen fast. For example, when you click a button or type in a box, JavaScript can respond right away.
JavaScript Engines
A JavaScript engine is a program that reads and executes JavaScript code. Computers cannot understand JavaScript directly, so engines convert the code into instructions the computer can follow. Every major browser has its own engine optimized for speed and performance. For example, Google Chrome uses the V8 Engine, which also powers Node.js for server-side development.
Mozilla Firefox runs SpiderMonkey, the first-ever JavaScript engine, while Apple’s Safari uses JavaScriptCore. These engines handle calculations, process logic, and keep scripts running efficiently.
The DOM (Document Object Model)
DOM is a structured representation of a web page. When a page loads, the browser converts HTML into a tree-like structure where each node represents an element like headings, paragraphs, images, or buttons. JavaScript can access this tree to modify content, change styles or rearrange elements dynamically.
For example, a script can update a product list without reloading the page or highlight a menu item when a user hovers over it. The DOM is essential for creating interactive web experiences and allows static HTML to behave like a fully functional application.
Events
Events are signals that indicate user interactions or system changes on a web page. JavaScript listens for these signals and executes code in response. Common events include clicks, keyboard inputs, mouse movements, and page loads.
For example, a form submission can trigger validation checks or typing in a search box can show real-time suggestions. Events are fundamental for creating responsive websites that react to user actions instantly, making web applications more engaging and usable.
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces)
APIs provide a set of tools and methods for JavaScript to perform tasks beyond the basic manipulation of web pages. Browser APIs allow access to device features such as cameras, GPS, or local storage. The Fetch API lets web pages retrieve or send data to servers without requiring a full reload, enabling dynamic content updates.
Third-party APIs expand functionality further by connecting to external services, such as displaying maps, weather, or social media feeds directly within a website. APIs make it possible to build interactive, data-driven applications that integrate seamlessly with other platforms.
Code Flow
Code flow refers to the order in which JavaScript instructions are executed. By default, scripts run sequentially, one line at a time, from top to bottom. Functions allow developers to group code into reusable blocks that only execute when called, improving organization and reducing repetition.
Modern browsers also check for errors before running code, helping catch mistakes early. Understanding code flow is crucial for writing predictable, efficient scripts and managing complex interactions in web applications.
JavaScript vs HTML vs CSS: Understanding the Difference
Many beginners wonder about the relationship between JavaScript, HTML and CSS. While these three technologies work together to build websites, they serve different purposes and have distinct roles.
| Feature | HTML | CSS | JS |
| Full Form | Hyper Text Markup Language | Cascading Style Sheets | JavaScript |
| Primary Role | Provides the structure and content of the page. | Controls the visual presentation and layout. | Adds behavior and interactivity to the page. |
| What It Does | Defines elements like headings, paragraphs, images and links. | Determines colors, fonts, spacing and positioning. | Makes the page respond to user actions, performs calculations and runs logic. |
| Language Type | Markup Language (Not a programming language). | Style Sheet Language. | True Programming Language. |
| Simple Analogy | The Skeleton: It holds everything together. | The Clothing: It makes the skeleton look good. | The Action: It makes the body move and react. |
| Practical Example | Creates a button on the screen. | Style the button with colors and fonts. | Makes the button perform an action when clicked. |
| Execution | Interpreted by the browser to display content. | Interpreted by the browser to apply styles. | Executed by the browser’s JavaScript engine to run logic. |
What Are the Best Ways to Learn JavaScript?
One of the best things about learning JavaScript is that you do not need to buy expensive software or download heavy files to get started. You likely already have everything you need right on your computer.
There are three main places where beginners can practice writing code.
1. The Browser Console (The Quickest Way)
Your web browser is not just for browsing the internet. It has a built-in tool called the ‘Console’ where you can write and run JavaScript instantly. This is perfect for testing small math problems or checking if a line of code works.
How to open it:
- Open Google Chrome, Firefox or Edge.
- Right-click anywhere on the page and select Inspect.
- Click on the Console tab at the top of the new window.
- Type alert(“Hello!”); and press Enter.
You will see a pop-up message immediately. This is the fastest way to verify your code.
2. Online Code Editors (No Setup Required)
If you want to save your work or share it with friends, online code editors are a great choice. These websites let you write HTML, CSS and JavaScript in one place and see the result instantly on the side. They act like a digital sketchbook for developers.
Popular free options include:
- CodePen: Great for making visual designs and small projects.
- JSFiddle: Simple and effective for testing code snippets.
- Replit: Excellent for running longer scripts and learning logic.
You just open the website, start typing and your code runs in the cloud.
3. Text Editors
When you are ready to build real websites or larger projects, you should move to a text editor installed on your computer. This allows you to write, organize and manage your code efficiently for full-fledged development tasks.
You have several options when it comes to writing JavaScript code. Popular editors like Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text, Atom, Brackets and Notepad++ make it easy to organize your files, highlight your code, and spot mistakes as you type. If you want a more feature-packed setup, IDEs like WebStorm offer advanced tools for managing larger projects and streamlining your workflow. Try a few of these options to see which one feels most comfortable for you as you build your projects.
How to Write The First JavaScript Program?
The best way to learn is by doing. In the programming world, your first milestone is always the “Hello, World!” program. It is a simple test to make sure your code is working correctly.
In Your Browser
You can write JavaScript directly inside an HTML file. This is how most websites run their scripts.
📄 The Code:
<h1>Check the console for the message!</h1>
// This is our first JavaScript program
console.log("Hello, World!");
Output:
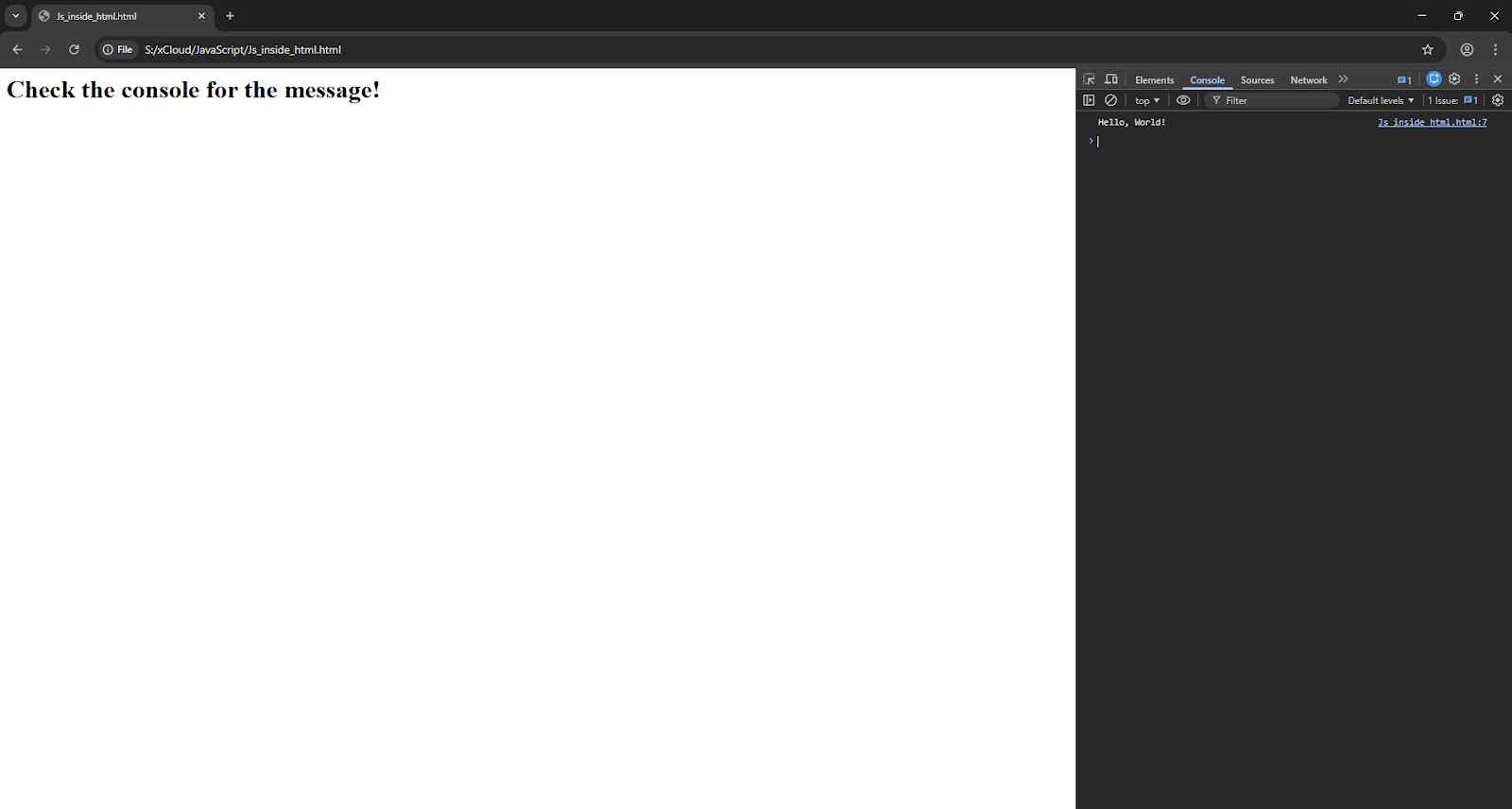
<script>: This tells the browser, ‘Hey, everything inside here is JavaScript code.’
Console.log(): This command sends a message secretly to the browser’s developer tools. You won’t see it on the page itself, but it appears in the Console tab we looked at earlier.
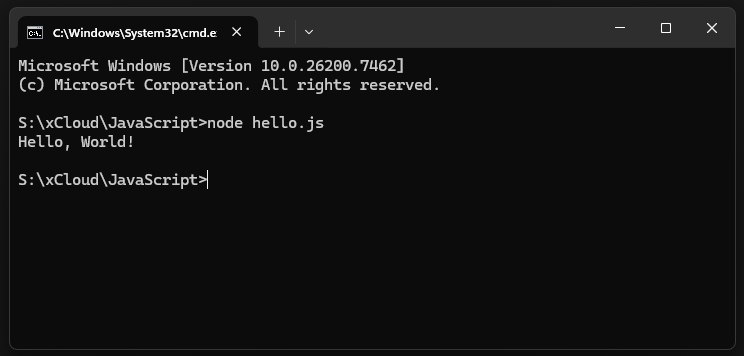
In the Server Terminal
If you have Node.js installed, you can run JavaScript on your computer without a browser at all.
📄 The Code (hello.js):
console.log("Hello, World!");Open your terminal or command prompt and type: node hello.js
Output:
Adding Comments
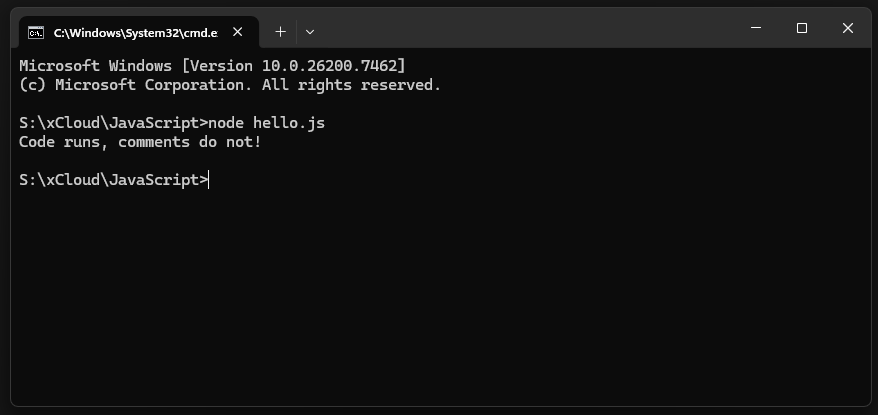
Sometimes you need to leave notes for yourself or other developers. JavaScript ignores these lines completely, so they will not break your program.
- Single-line comments: Use two forward slashes //.
- Multi-line comments: Wrap your text in /* and */.
Code:
// This is a note for a single line
/* This is a longer note that
spans across multiple lines
*/
console.log("Code runs, comments do not!");Output:
The Building Blocks of JavaScript
Learning JavaScript starts with mastering a few fundamental concepts. These are the building blocks that will appear in almost every script you write, whether it is a small feature or a massive application.
Variables
Variables are like containers that store information for your program to use later. In JavaScript, modern code typically uses let and const to declare these containers.
- let: Used for values that might change later (like a score in a game).
- const: Used for values that stay the same (like your birthday).
💻 Example:
let userName = "Alex"; // This can be changed
const daysInWeek = 7; // This stays fixed
console.log(userName); // Output: Alex
userName = "Sam"; // Changing the value
console.log(userName); // Output: SamData Types
JavaScript works with several different types of data. You do not always need to tell JavaScript what type you are using; it figures it out for you.
- Strings: Text wrapped in quotes.
- Numbers: Integers or decimals.
- Booleans: Simply true or false (used for logic).
💻 Example:
let price = 99.50; // Number
let greeting = "Hello!"; // String
let is UserLoggedIn = true; // BooleanFunctions
Functions are reusable blocks of code. Instead of writing the same instructions over and over, you define a function once and “call” it whenever you need it. This keeps your code clean and organized.
💻 Example:
// Defining the function
function greetUser(name) {
return "Welcome back, " + name + "!";
}
// Calling the function
console.log(greetUser("Sarah")); // Output: Welcome back, Sarah!
console.log(greetUser("Mike")); // Output: Welcome back, Mike!Conditional Statements
Conditional statements allow your code to make decisions based on certain conditions. Using if and else, you can specify which actions should run when a condition is true and what should happen when it is false. This helps your programs respond dynamically to different situations.
💻 Example:
let batteryLevel = 10;
if (batteryLevel < 20) {
console.log("Please charge your device.");
} else {
console.log("Battery is sufficient.");
}Loops
Loops help you repeat actions without writing the same code repeatedly. The most common one for beginners is the ‘for’ loop, which runs a specific number of times.
💻 Example:
// Count from 1 to 5
for (let i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
console.log("Count: " + i);
}Events
Events are what make websites feel alive. They trigger JavaScript code when a user does something, like clicking a button or pressing a key. Without events, a website is just a static digital poster.
💻 Example:
// This runs when a button with ID "myButton" is clicked
document.getElementById("myButton").addEventListener("click", function() {
alert("Button clicked!");
});
These fundamentals are the vocabulary of JavaScript. Start by practicing these simple scripts in your browser’s console and you will quickly build the confidence to write more complex programs.
What Are JavaScript Libraries And Frameworks?
Once you grasp the basics, you rarely need to build everything from scratch. Professional developers rely on JavaScript libraries and frameworks to work faster and make fewer mistakes. These are collections of pre-written code that act like superpowers for your development process.
JavaScript Libraries vs Frameworks
You do not need to write every single line of code from scratch. Professional developers rely on pre-written code collections to work faster. These collections come in two main types and the difference between them is easy to spot if you use a simple comparison: the Toolbox versus the Factory.
Libraries: A library is a collection of pre-written code that helps you solve specific problems without writing everything from scratch. It provides ready-made functions and tools that you can integrate into your project to handle common tasks efficiently, saving time and reducing errors.
Example: jQuery is a famous library. You might use it just to make a button animation smoother but the rest of your website stays exactly the same.

Frameworks: A framework works more like a factory. It gives you the blueprints, the foundation and the rules for the entire building. It tells you where to put the walls and how to organize the rooms. When you use a framework, you have to follow its rules to build your application.
Example: React, Angular and Vue are popular frameworks. Companies use these to build massive, complex apps like Facebook or Netflix because they keep everything organized.
Why Developers Use These Tools
You might wonder why you should learn extra tools if you already know JavaScript. The answer is simple, efficiency. Writing every single line of code from scratch is like trying to build a house by making every individual brick yourself. It is possible, but it takes forever and is easy to mess up.
Libraries and frameworks give you the bricks, the windows and the doors ready to go. You just have to put them together. Main reasons to rely on them:
Speed: They handle the boring, repetitive parts of coding for you. This means you can finish projects in days instead of months.
Consistency: Frameworks force you to write code in a tidy, organized way. If you work on a team, this ensures everyone follows the same rules and understands each other’s work.
Reliability: These tools are used by millions of developers. They have been tested and fixed over and over again, so they are much less likely to have bugs than code you write entirely on your own.
Community Help: Popular frameworks have massive communities. If you get stuck, you can almost always find a solution online because someone else has likely faced the exact same problem.
Where to Start Learning JavaScript?
You do not need to spend money to learn JavaScript. The web is full of high-quality, free resources that are just as good as paid courses. Whether you like reading manuals or playing with code directly, there is a perfect starting point for you.
📖 The Official Guide — MDN Web Docs: If you want the most accurate and complete information, look no further than the MDN Web Docs by Mozilla. Developers consider this the ‘bible’ of web development.
📖 The Interactive Playground — W3Schools: If you learn by doing, W3Schools is a fantastic choice. Their tutorials break complex topics into tiny, manageable steps.
📖 The Community Hub — JavaScript.com: For a mix of everything, check out JavaScript.com. It is a great hub created by the community to help new learners find their way.
Your 4-Step Action Plan
Reading is helpful but practice is what makes the skills stick. Follow these simple steps to build your confidence:
- Read the Basics: meaningful syntax and rules from one of the sites above.
- Play in the Console: Open your browser’s developer tools and write small snippets of math or text logic.
- Build Something Real: Creating a simple project, like a digital clock or a To-Do list, teaches you more than any book.
- Join the Conversation: Connect with others on coding forums or Discord channels. Asking questions is a fast way to learn.
Consistency is your best friend here. Even 20 minutes of coding a day is better than studying for five hours once a week.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of JavaScript
JavaScript powers a large portion of the interactive web and is widely used by developers around the world but it has advantages and limitations that beginners should know. Understanding these can help decide when to use plain JavaScript and when to explore modern versions or frameworks like Node.js, Vue.js or React.
Pros of JavaScript
JavaScript offers many benefits that make it a key language for the web:
- Interactive Web Pages: JavaScript makes websites responsive, allowing buttons, forms, and animations to react instantly to user actions.
- Runs Everywhere: It works on all major browsers without additional installations.
- Versatile Language: Developers can use JavaScript for frontend and, with Node.js, for backend development as well.
- Rich Ecosystem: A wide range of libraries and frameworks like Vue.js, React and Angular make development faster and easier.
- Quick Learning Curve: Beginners can start with simple scripts and gradually build up to complex applications.
Cons of JavaScript
JavaScript has some limitations that developers should keep in mind:
- Browser Dependence: JavaScript relies on the browser, so differences between browsers can cause unexpected behavior.
- Security Risks: Being client-side, JavaScript code can be seen and manipulated by users, requiring careful handling.
- Performance Issues: Large JavaScript applications may run more slowly without proper optimization.
- Complexity in Advanced Projects: As applications grow, managing plain JavaScript can become harder without frameworks or runtime environments.
Moving to Modern Versions
If these limitations become challenging, beginners or developers can explore updated versions and frameworks:
- Node.js allows JavaScript to run on servers, opening backend development opportunities.
- Vue.js and other frontend frameworks help manage complex user interfaces more efficiently.
- React and Angular provide component-based approaches that simplify large project maintenance.
What Are The Common JavaScript Myths?
When you start learning web development, you will hear a lot of rumors. Some of these can make the language seem scarier than it actually is. Let us look at the facts and bust the biggest myths preventing beginners from starting.

Myth #1: JavaScript and Java Are the Same
This is the single most common mix-up in the tech world. You might think they are related because they share a name, but they are completely different tools. A popular saying among developers is that Java and JavaScript are as related as ‘Car’ and ‘Carpet.’
Java: This is a complex, strict language. It requires a “compiler” to process code before it runs. It is mostly used for massive banking systems, enterprise software, and Android apps.
JavaScript: This is a flexible scripting language built for the web.3 It runs directly in your browser without any extra steps.
The confusing name was actually a marketing trick. In the 1990s, Java was very popular, so the creators named their new language “JavaScript” to ride on its success.
Myth #2: JavaScript Is Only for Front-End
For a long time, this was true. JavaScript lived only inside the web browser and handled things like animations or button clicks. But that changed completely with the arrival of Node.js.
Now, you can use JavaScript to build the ‘back-end’ of a website too. This means you can write code that runs on the server, talks to databases and handles user accounts. You can essentially build an entire application front and back using just this one language.
Myth #3: You Need to Be a Math Genius
Many people avoid coding because they think it involves complex calculus or algebra. The truth is much simpler. Web development is mostly about logic, not math.
If you can understand a basic sentence like ‘If the user is logged in, show the profile button; otherwise, show the login button,’ you already have the skills to write JavaScript. You will mostly use basic arithmetic (addition and subtraction) and logical thinking rather than complex equations.
Ready to Bring the Web to Life?
JavaScript is more than just a programming language; it is the tool that turns static pages into living experiences. You now understand how the engine works, how the DOM acts as a map and how functions make things happen. From simple buttons to full applications, you now see the potential in your hands.
If you have found this blog helpful, feel free to subscribe to our blogs for valuable tutorials, guides, knowledge and tips on web hosting and server management. You can also join our Facebook community to share insights and take part in discussions. And do not forget to share what you have built. We would love to see your work.