Deploying an can often involve complex configurations and server management tasks. With xCloud, this process becomes simple, automated, and developer-friendly.
xCloud provides an intuitive interface that allows you to easily deploy, manage, and scale your Node.js applications directly from your Git repository without worrying about manual setup or infrastructure maintenance.
Follow the guide to deploy your Node.js application easily with xCloud:
Step 1: Choose the Application #
To begin deployment, click on the ‘Create Site’ button from the dashboard. You will then be asked to choose ‘Server’ from the dropdown.
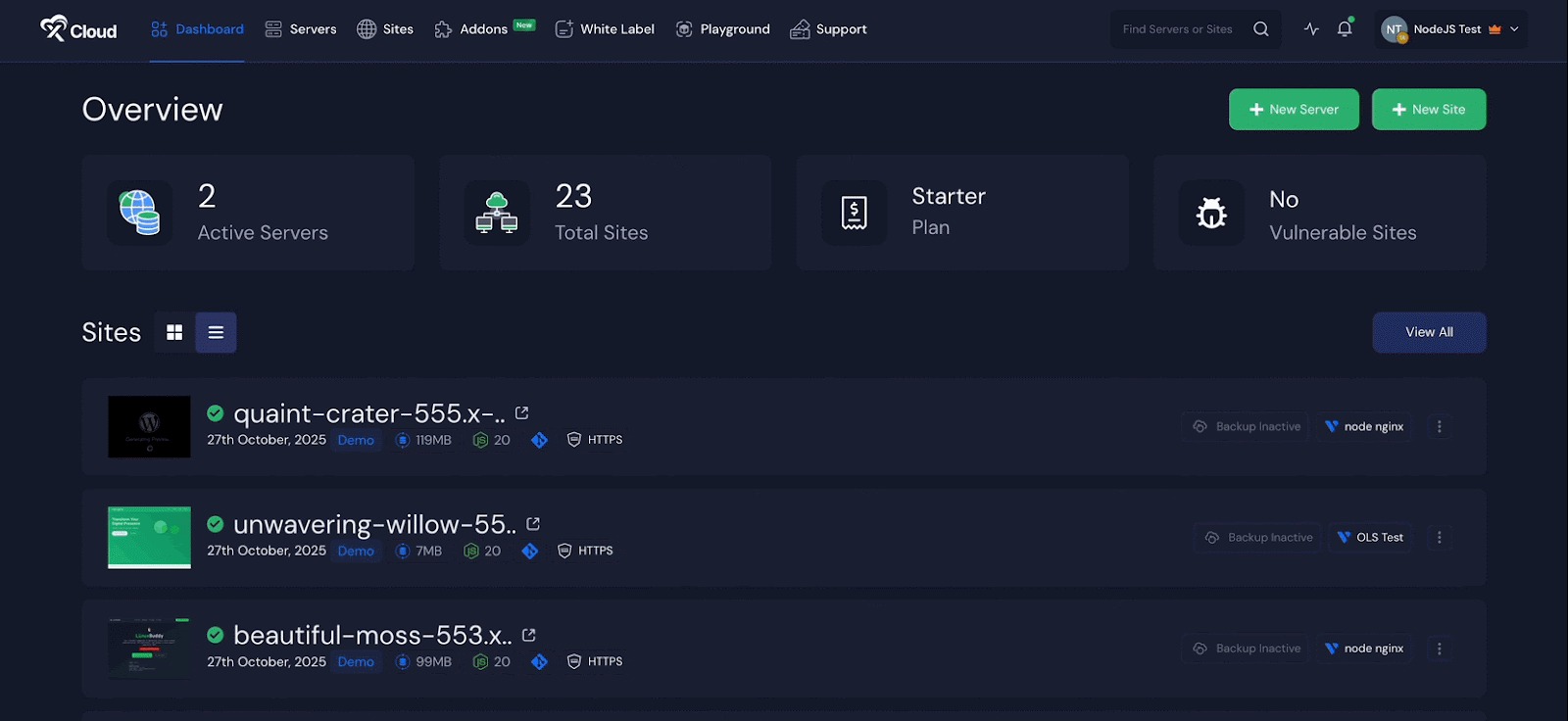
Next, you will see options such as ‘WordPress’ and ‘Custom PHP’. Go to the ‘Node.js’ option from the tab. After that, choose the ‘Clone a Git Repository’ option to import your Node.js application using a Git provider.
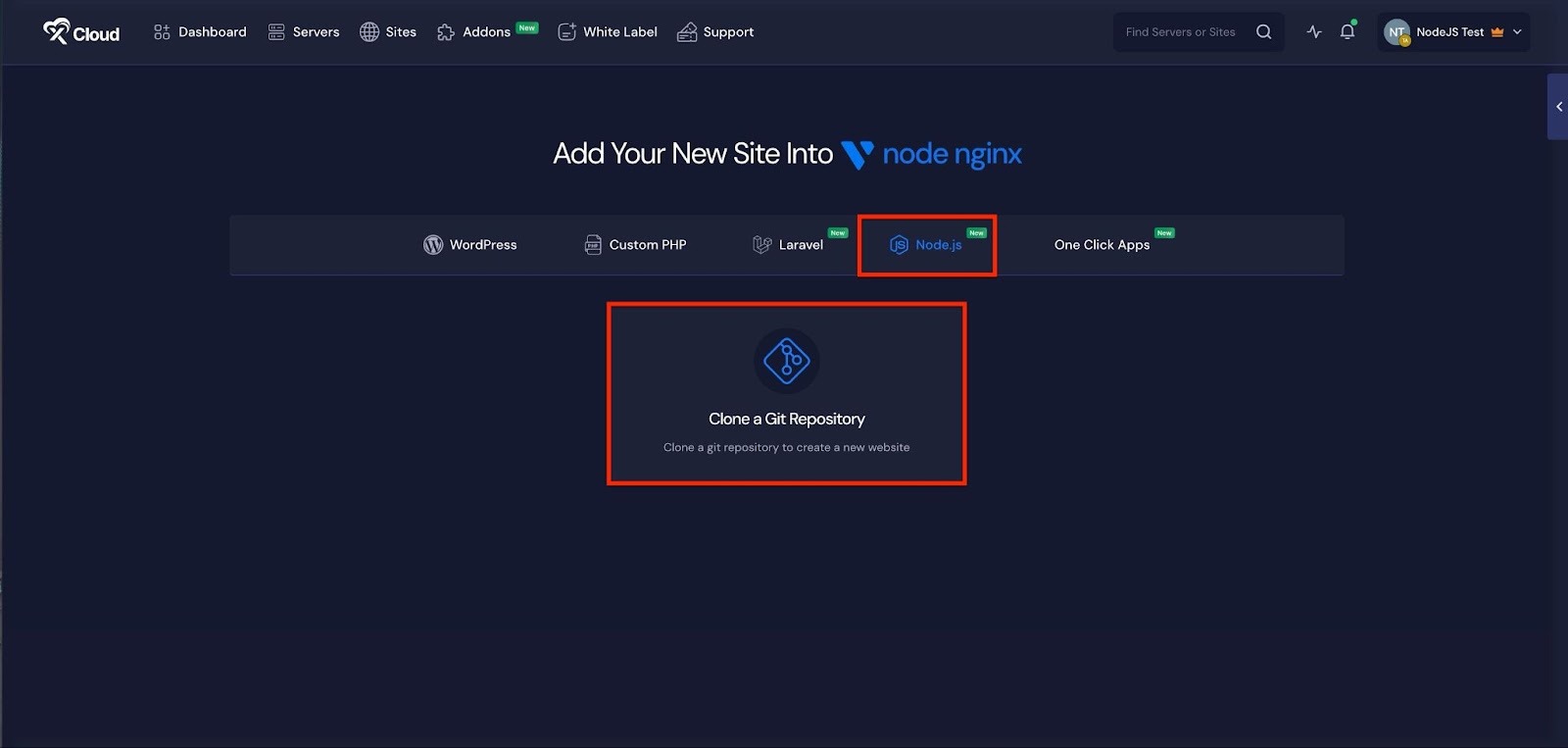
Step 2: Set Up Domains #
The ‘Domains’ tab allows you to configure your site’s domain. You can either create a ‘Demo Site’ or a ‘Live Site’. For this documentation, we’ll proceed with the ‘Demo Site’ option and click ‘Next’ to continue.
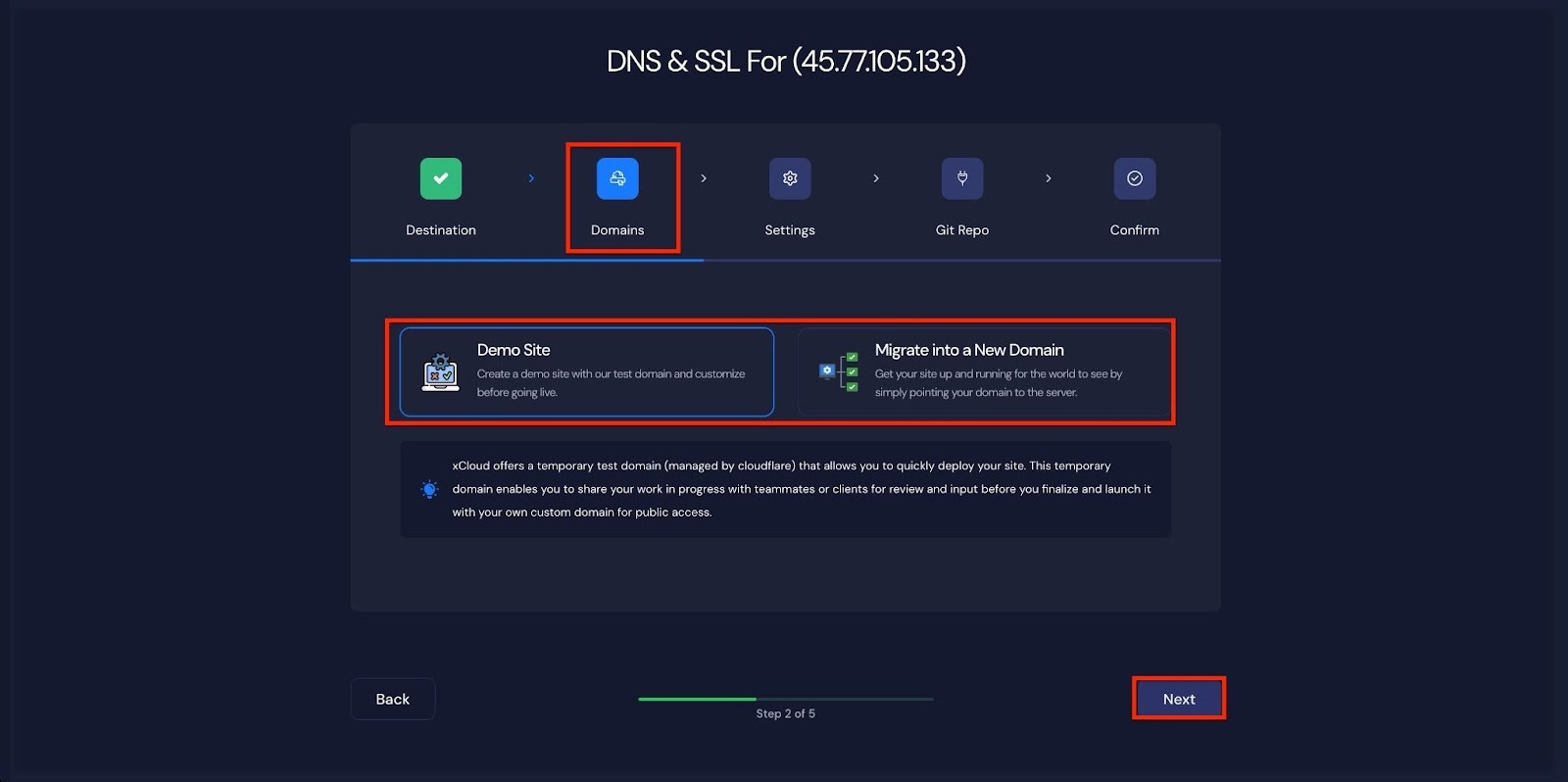
Step 3: Configure Node.Js Application #
In the ‘Settings’ tab, you will find options to configure the Node.js version and manage site users. Adjust them according to your preferences.
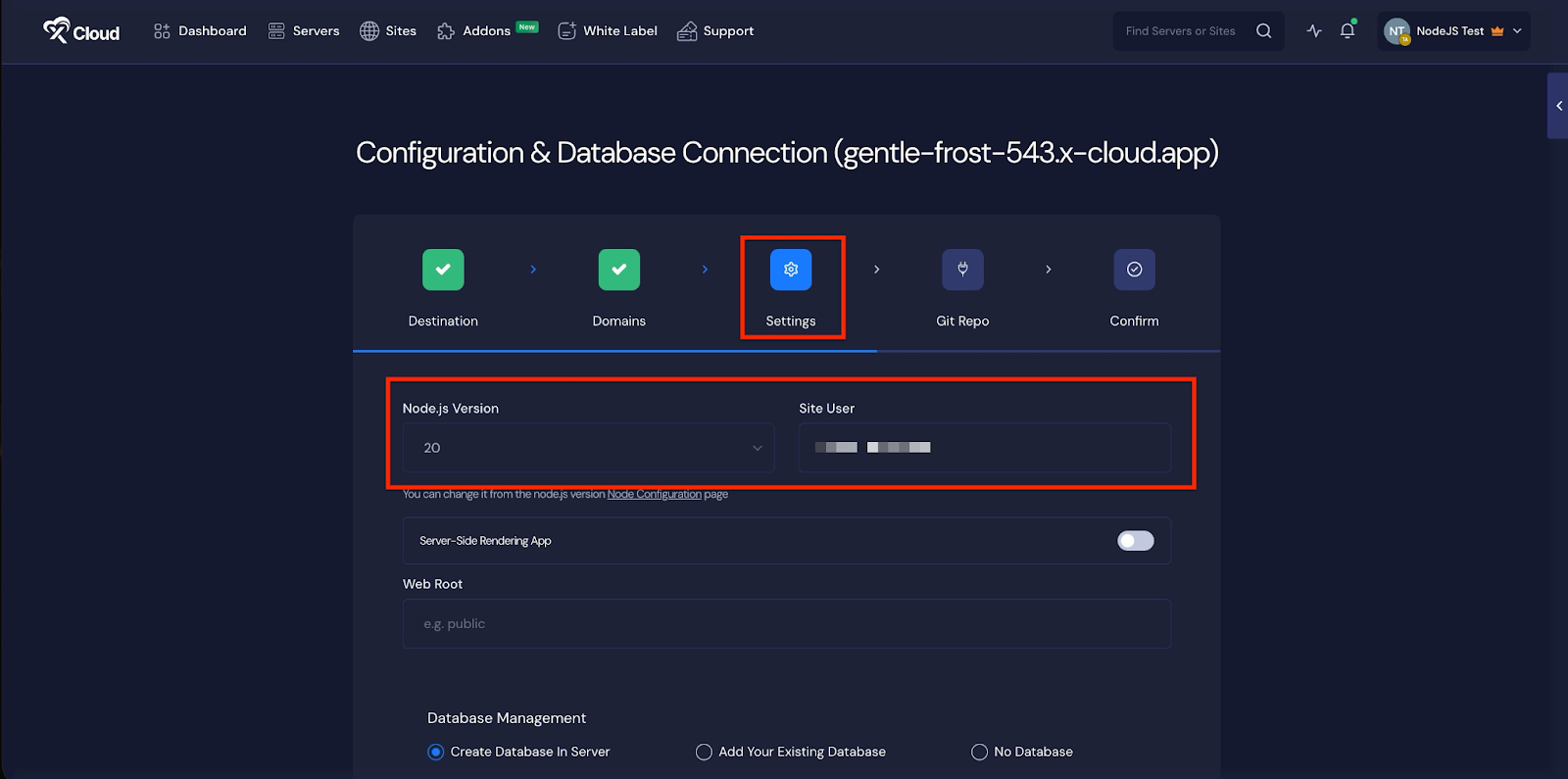
Next, you will see the ‘Server-Side Rendering App’ option. To proceed with a ‘Client-Side Rendering App’, keep the toggle off. To deploy a ‘Server-Side Rendered App’, toggle it on.
– Client-Side Rendering (CSR): #
If your application is built using frameworks like React or Vue that render content in the browser, keep the toggle off. In this mode, the server mainly serves static files, and all rendering happens on the client side.
– Server-Side Rendering (SSR): #
If your Node.js application (for example, Next.js or Nuxt.js) renders pages on the server before sending them to the client, toggle this option on. This allows xCloud to configure the environment to support SSR processes properly.
Here we are proceeding with deploying a ‘Server Side Rendered App’ option
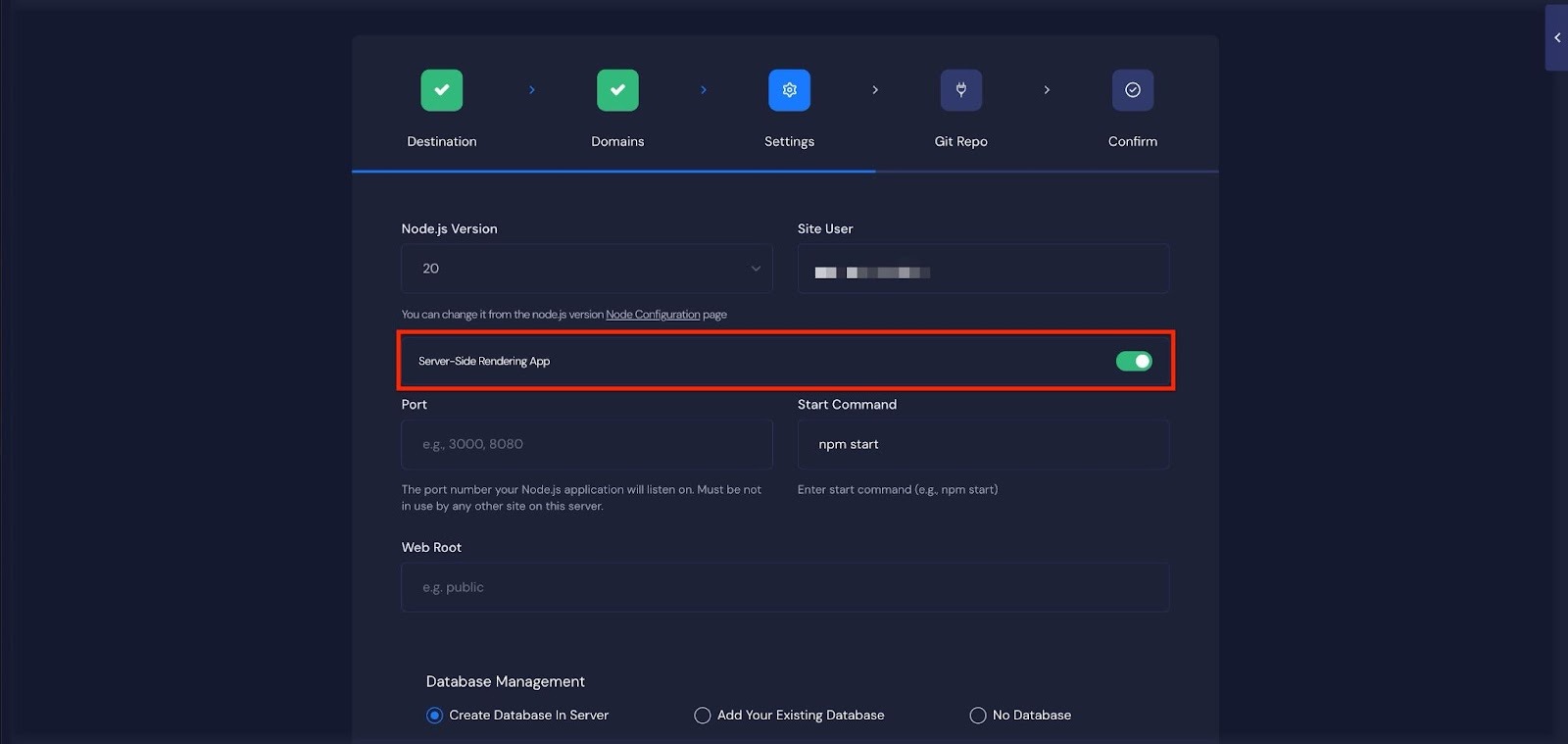
Then you’ll need to provide a few essential details:
→ Port:
Enter the port number your Node.js application listens on (e.g., 3000 or 8080). xCloud uses this port to connect incoming traffic to your app.
→ Start Command:
Specify the command that runs your application (for example, npm start, node server.js, or yarn dev). This tells xCloud how to start your Node.js server after deployment.
→ Web Root Path:
If your project’s main application files are located in a subdirectory (for instance, /app or /src), enter that path here. If your app is in the root directory, you can leave this field blank.
Now, insert the ‘Port’ and ‘Start Command’ in the respective fields. You can also specify a ‘Web Root’ Path for your application.
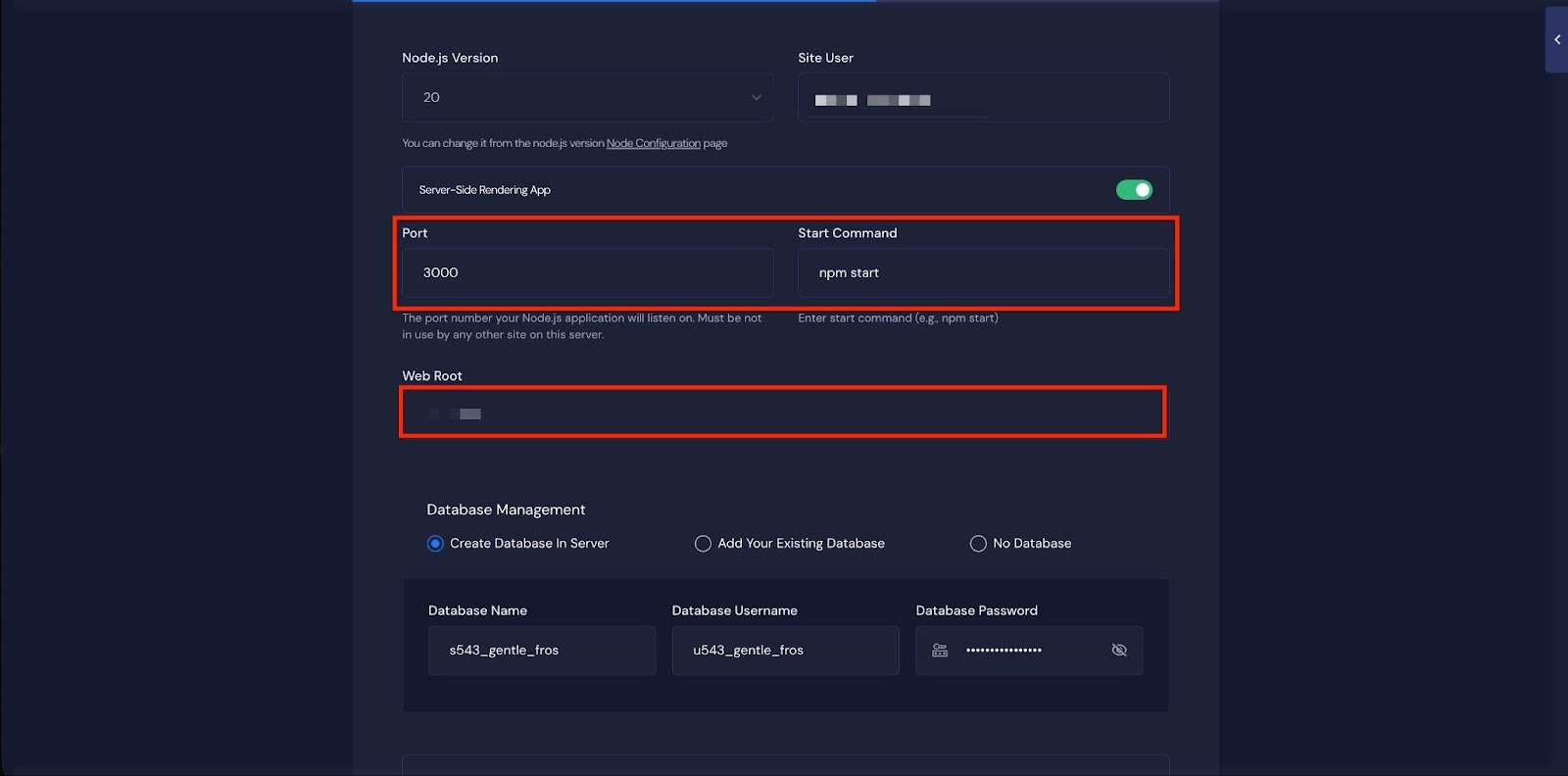
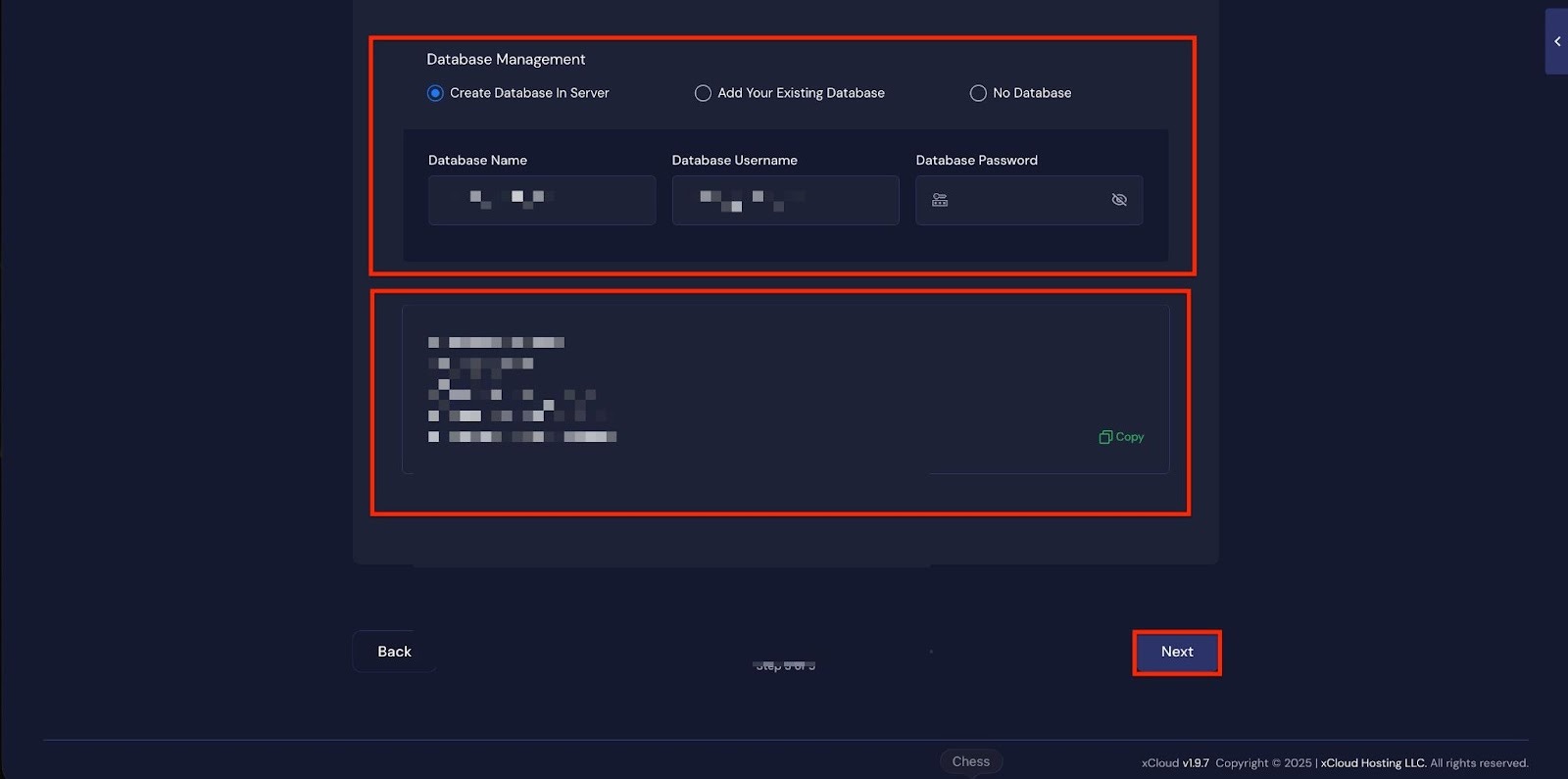
In the following step, you can choose one of the database options ‘No Database’, ‘Add an Existing Database’, ‘Create a New Database’ directly on the server. Once selected, click ‘Next’.
Step 4: Insert Git Repository Credentials #
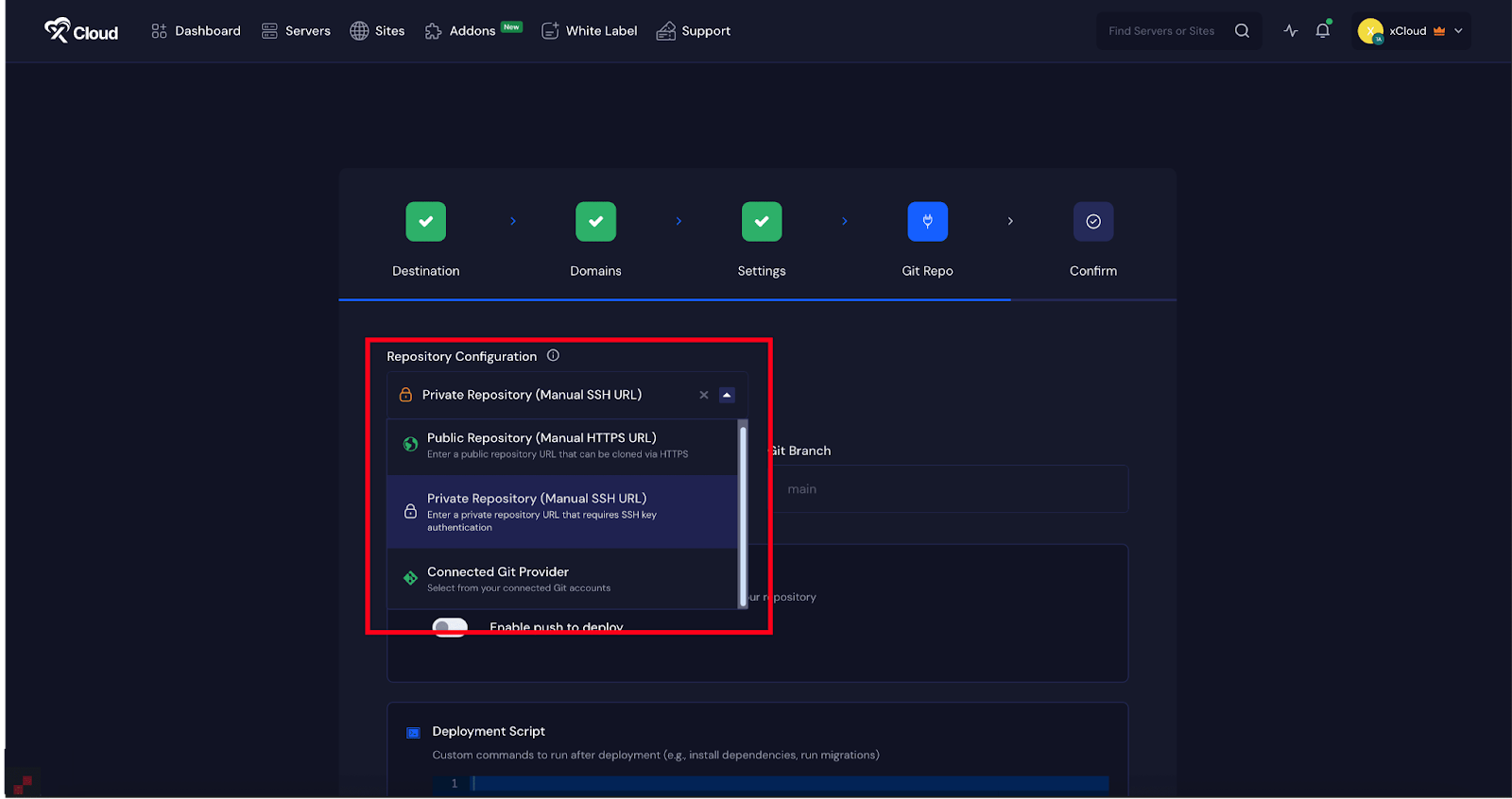
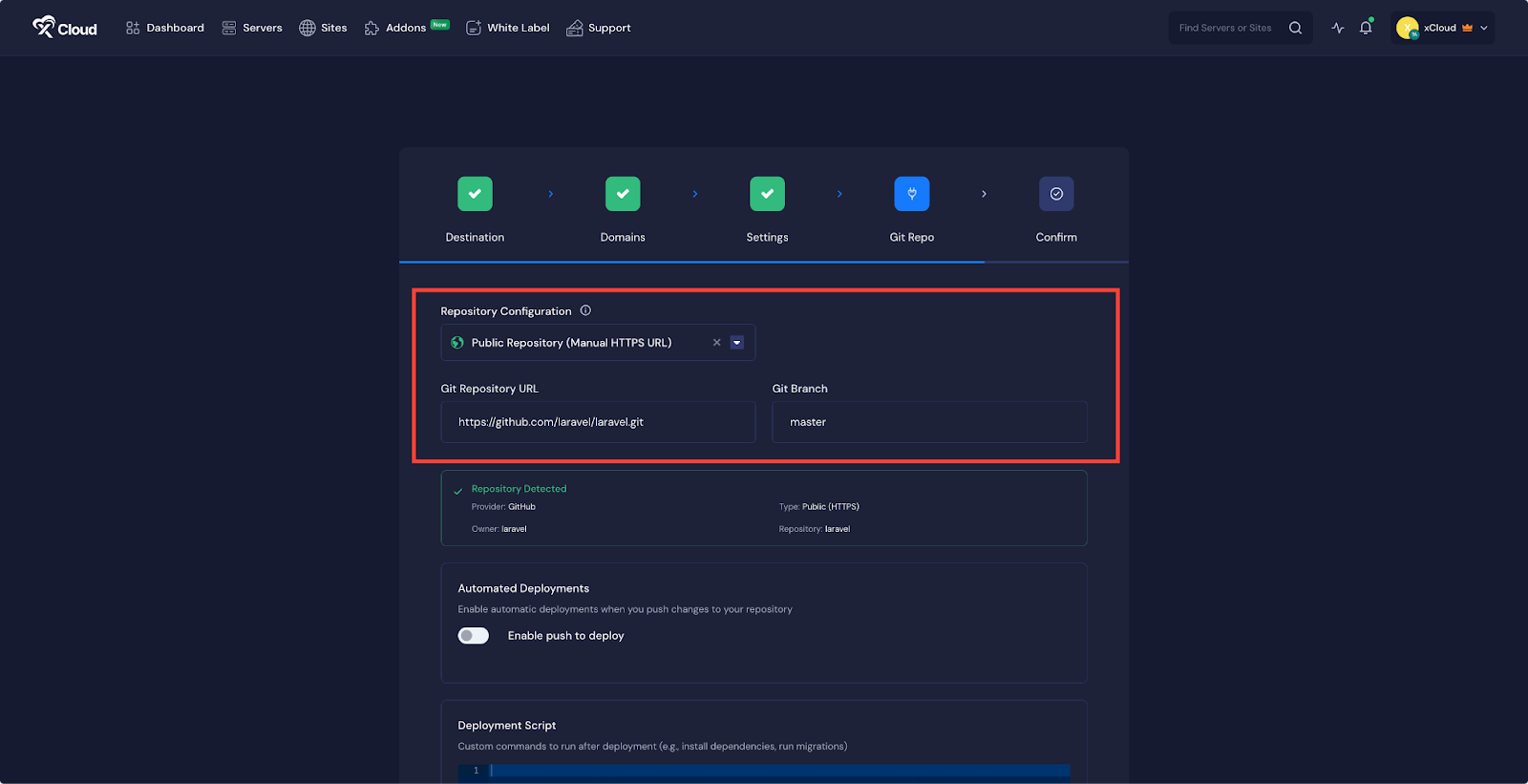
In the “Git Repo” tab, you will find three repository options ‘Private Repository (Manual SSH URL)’, ‘Public Repository (Manual HTTPS URL)’, ‘Connected Git Provider’.If you choose Public Repository (Manual HTTPS URL), enter your GitHub Repository URL and specify the Git Branch.
Note: Copy the HTTPS URL from your GitHub repository dashboard.
If you choose Private Repository (Manual SSH URL), enter your GitHub Repository SSH URL and specify the Git Branch.
Note: Copy the SSH URL from your GitHub repository dashboard.
In this document, we’ll deploy the project using the “Git Provider” option.
Choose “Connected Git Provider” from the dropdown menu. From the “Select Git Provider” list, choose the connected account you want to use. Then, browse through the repositories, select the one you want to deploy, and choose the specific branch of that project.
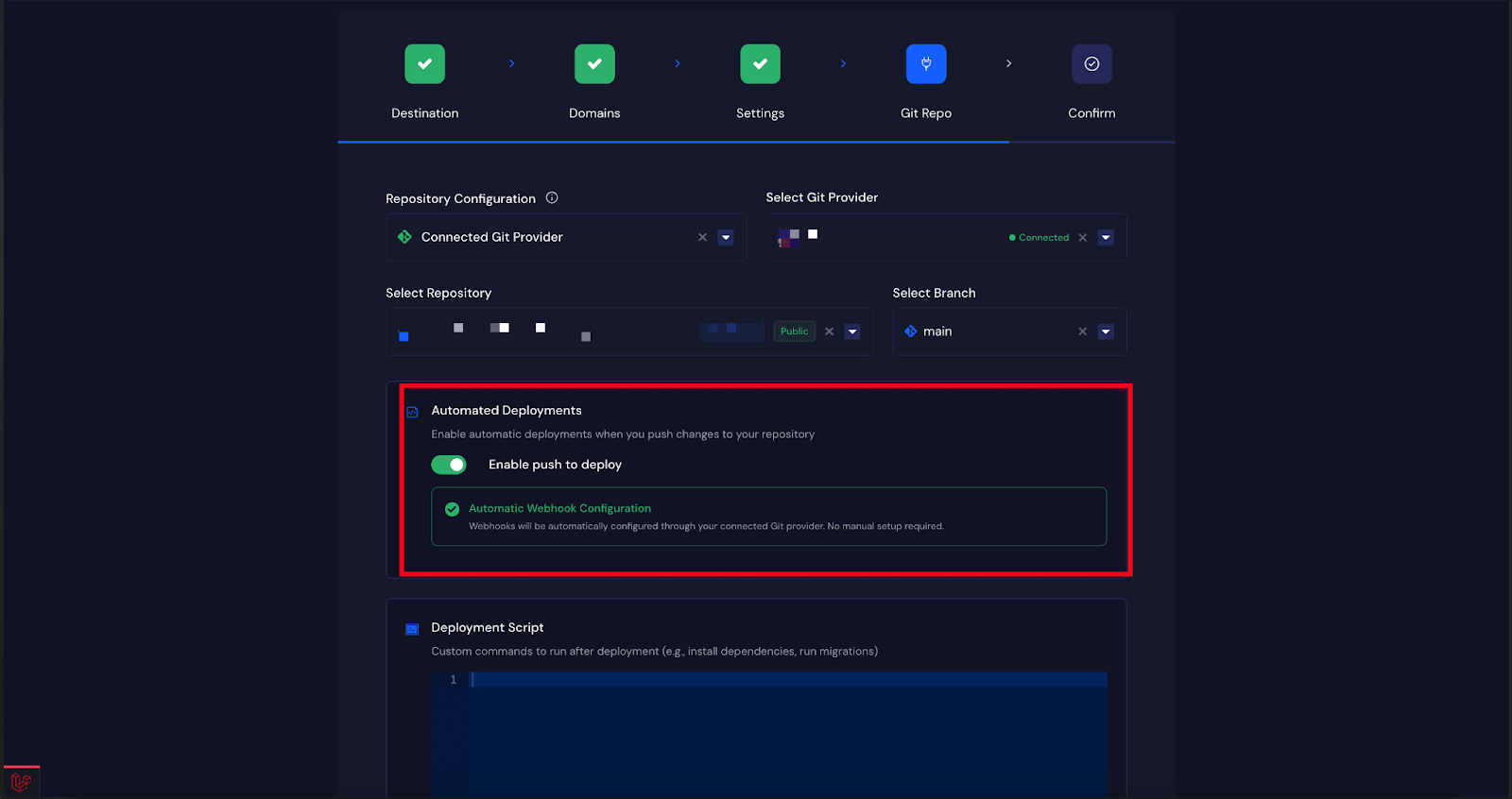
Step 5: Enable Push-to-Deploy #
The next step is to enable automated deployment. Toggle on the “Enable Push to Deploy” option. Copy the ‘Deployment URL’ provided here, you will need to insert it into your GitHub repository’s webhook settings.
Step 8: Run Deployment Script #
Once the repository integration is complete, you can configure post-deployment actions.
In the ‘Deployment Script’ field, enter any custom commands you want to execute after deployment. You can also select one of the example scripts provided. After configuring this, click ‘Next’ to continue.
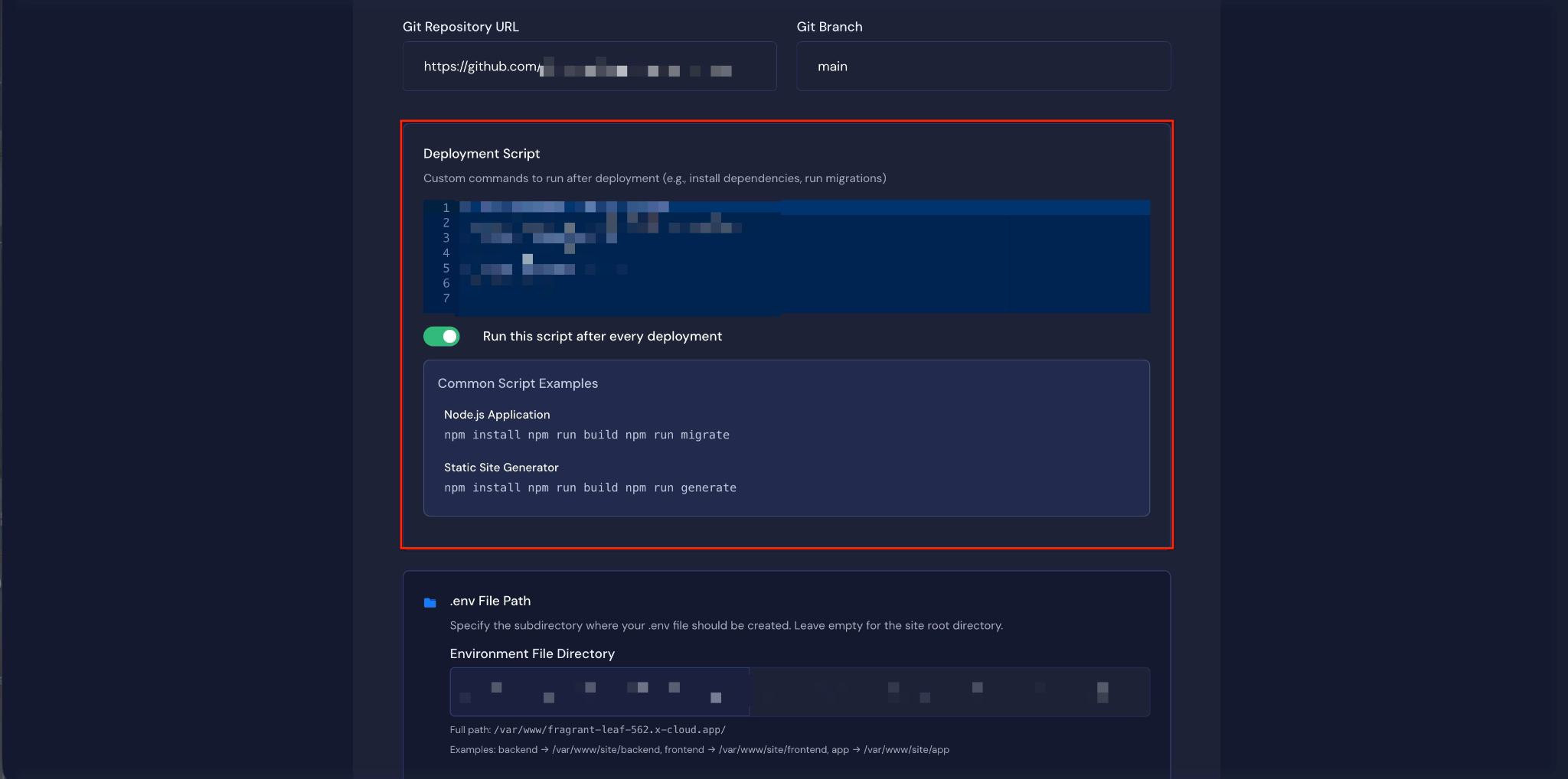
Next, you can specify the subdirectory where your .env file should be created in the “.env File Path” field. You can also enter the contents of your .env file in the “File Content” field.
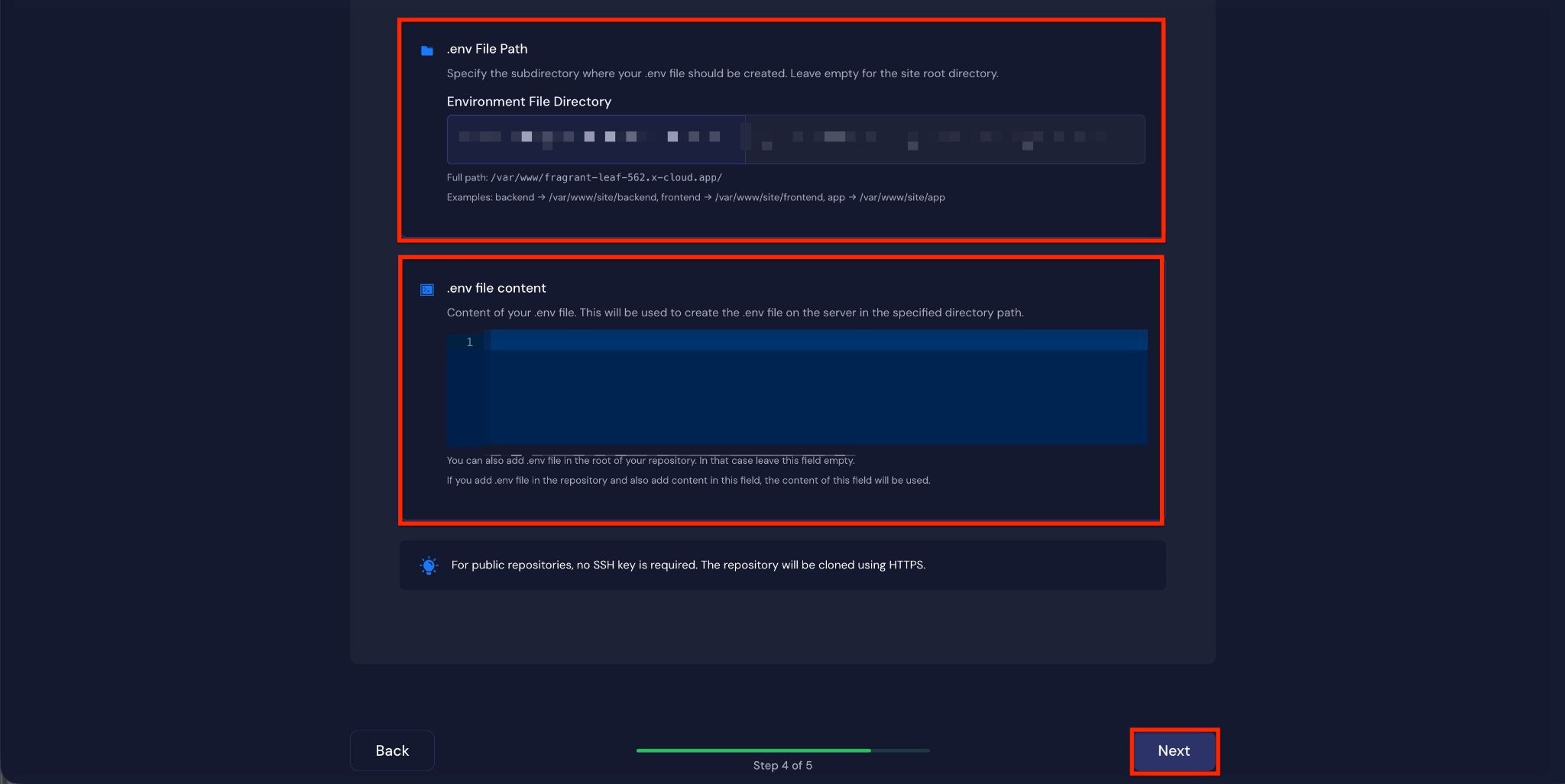
Step 9: Confirm Deployment #
The final step is to confirm and start the deployment. Click the ‘Start’ button to begin the process. You can monitor the deployment progress in real time.
Once the deployment is complete, a success message will appear. From there, you can access your site dashboard.
After deployment, visit your site to confirm that your Node.js application has been successfully deployed with xCloud.
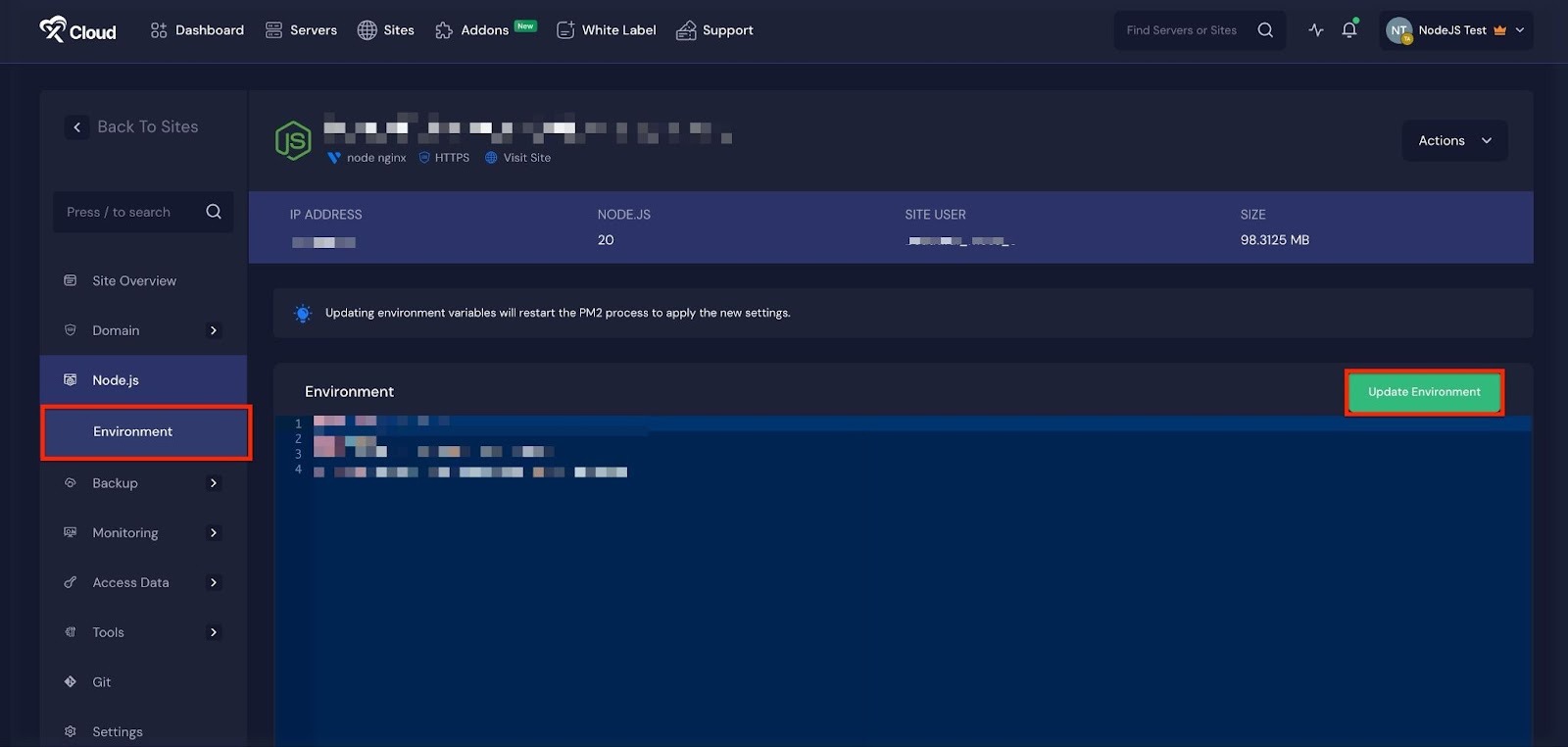
Environment Editor for Node.Js Application #
The Environment section in xCloud allows you to customize configuration settings for your n8n instance. Just go to the ‘Environment’ option from the sidebar and adjust as you need then click on the ‘Save’ button.
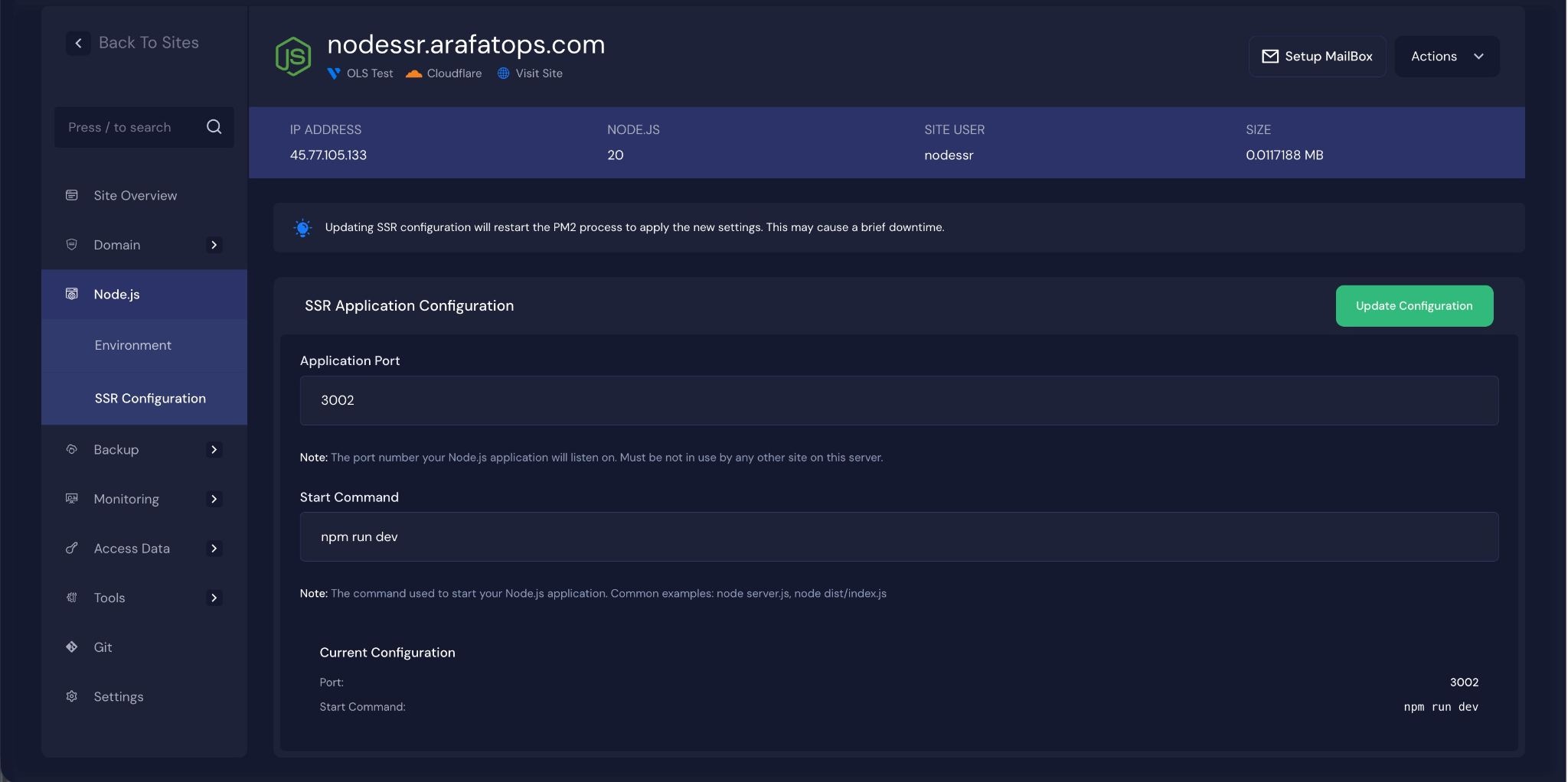
SSR Configuration for Node.js application #
If you are deploying an SSR application, you can update the ‘Application Port’, ‘Start Command’ later as well. Just go to the ‘SSR Configuration’ from the ‘Node.js’ Menu under the site dashboard and click on the ‘Update Configuration’ button.
Deploying a Node.js application with xCloud is a streamlined and efficient process that eliminates the complexity of manual configuration and server management. Once your deployment is complete, you can easily manage your application, update configurations, and push new changes directly from your Git repository.
With xCloud, developers can focus on building and improving their Node.js applications while xCloud takes care of the infrastructure behind the scenes.
Still stuck? Contact our support team for any of your queries.